This article highlights the important of Network revenue. Networks that are unable to sustain their development through revenue require potentially enormous fund raises to stay viable. Only the strongest will survive the recession.
How do Crypto Networks make Money?
It is important to note that most digital assets are run by a network, and not a single entity or small party. This is the distinguishing factor between a company, and a blockchain network or project. Once the blocks are set in motion, and the code and protocol rules are set, the everyday users form the network. The most popular example of this is Bitcoin. Once the Bitcoin blocks were set in motion, the anonymous founder Satoshi Nakamoto no longer controlled the network. Bitcoin was decentralized almost immediately with a small group of miners participating in the network. As Bitcoin continued to grow, so did the network effect.
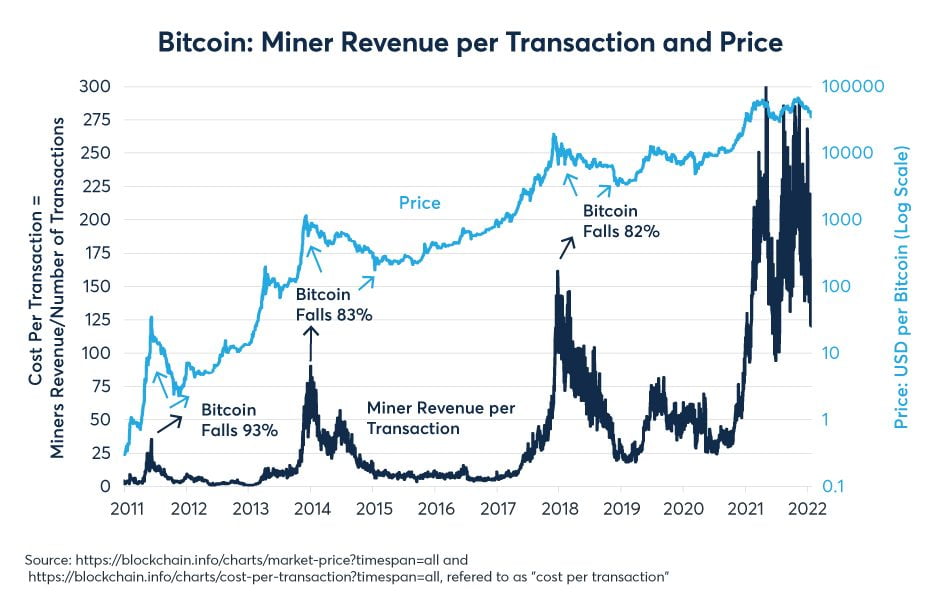
Bitcoin participants make money in two ways. Block rewards, which are achieved from mining Bitcoin, and Bitcoin network fees, which are achieved through validating transactions. Looking at the table from Messari, it is easy to see that Bitcoin revenue is highest during upward markets. Bitcoin transaction fees also take up more of the total revenue when markets are hot and active. Smart mining companies sold some Bitcoin and saved cash during the upward market, this set them up for success during the long bear market. By increasing computer efficiency, and renewable energy sources, Bitcoin miners can increase their net profits, while reducing expenses. Bitcoin continues to be profitable despite the large market downtrend. Companies that are positioned to hold large quantities such as Marathon Digital will be positioned well over the next 5 years.
Smart Contract Platforms make money in a variety ways. Ethereum was a prime example with mining much like Bitcoin. Ethereum recently switched to proof-of-stake which highly reduces energy expenses. Proof-of-stake networks create revenue for the protocol by validating transactions through the PoS consensus mechanism. Conesus is a fancy way of saying that the network agrees a transaction is valid. Network validators stake enormous amounts of a given token by locking it up for a reward over-time.
Let’s use Avalanche as an example. For those who have been reading along, you will notice many of our favorite crypto tokens are in the chart below. Fundamentally strong Networks are self-sustaining, with strong built in economic standards. Avalanche uses the PoS consensus as well, therefore validators do not need to spend as much money on equipment. Their initial investment is purely in the AVAX token. These tokens are then locked up for a reward over time, with built in inflationary rewards of more AVAX tokens. Validators not only receive these inflationary rewards, but they receive network fees over time. With the subnet upgrade, more AVAX tokens are required to be locked away to run specific blockchain needs such as gaming or NFT functions.
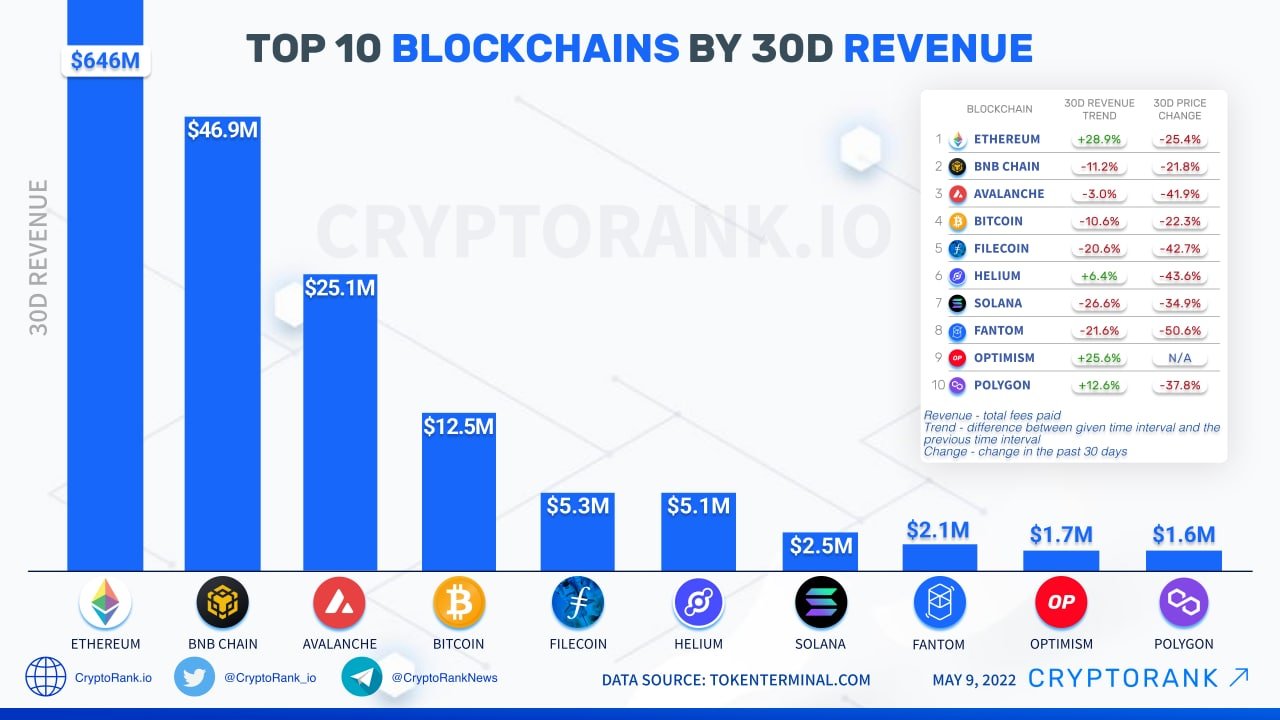
With more tokens locked, less are available for trade, this offsets the inflationary token economy. AVAX also has a burning mechanism, the more AVAX fees, the more AVAX tokens are removed from the supply permanently. AVAX furthers this by having a capped supply. Eventually, if the Network is successful, the tokens will become scarcer over time. During times of low price action validators are incentivized to hold tokens and avoid selling. During upward markets, some AVAX tokens should be sold to cover expenses. Since electricity is far less expensive for Avalanche validators when compared to Bitcoin, the carbon footprint is also low.
NFT Marketplaces earn revenue from volume. Looking at the chart above, Opensea dominates the application revenue for Crypto NFTs. Although behind Ethereum, Opensea is simply one application, and a private company. Opensea differentiates itself from the other examples in that it is not decentralized. Opensea makes money from a fee that is charges with each NFT trade. Opensea along with the owner of the collection receive a fee every time the NFT is traded. The artist receives a royalty fee, while Opensea receives a service fee for the use of the platform.
Many decentralized versions of Opensea are sprouting up, from Looksrare on Ethereum, to Magic Eden on Solana. Decentralized marketplaces create revenue from protocol fees. In some cases, marketplace tokens are utilized to assist with protocol revenue. Other examples simply take a percentage as a service fee and stockpile the returns within the protocol treasury. As with all digital asset treasuries, what Projects do with the fees is usually determined from a mix of a non-profit foundation, and governance (on chain voting).
Many popular crypto projects/networks have an associated non-profit foundation who’s soul purpose is to expand and upgrade the respective network. Fundamentally strong treasuries hold a basket of assets including stable coins for network longevity. Only the strongest, most forward thinking networks will survive this recession. It is important to question how a Network earns revenue when deciding whether or not to jump into it as an investment. Please remember none of this is financial advice, stay safe out there!
















